A discrete GPU is a dedicated graphics card for high-performance graphical tasks. When idle, it conserves energy and reduces heat by operating at lower power levels.
Understanding Discrete GPUs and Idle States:
What is a Discrete GPU?
A discrete GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) is a dedicated graphics card designed specifically for rendering visuals and handling complex graphical computations on a computer.
Unlike integrated GPUs, which share resources with the CPU and are integrated into the motherboard, discrete GPUs have their own dedicated memory and processing units.
This setup allows them to deliver higher performance, making them essential for tasks such as gaming, video editing, and 3D rendering.
Discrete GPUs are known for their powerful performance, and they are crucial for applications that require high graphical processing power, such as virtual reality (VR) and artificial intelligence (AI) computations.
Idle State: What Does It Mean?
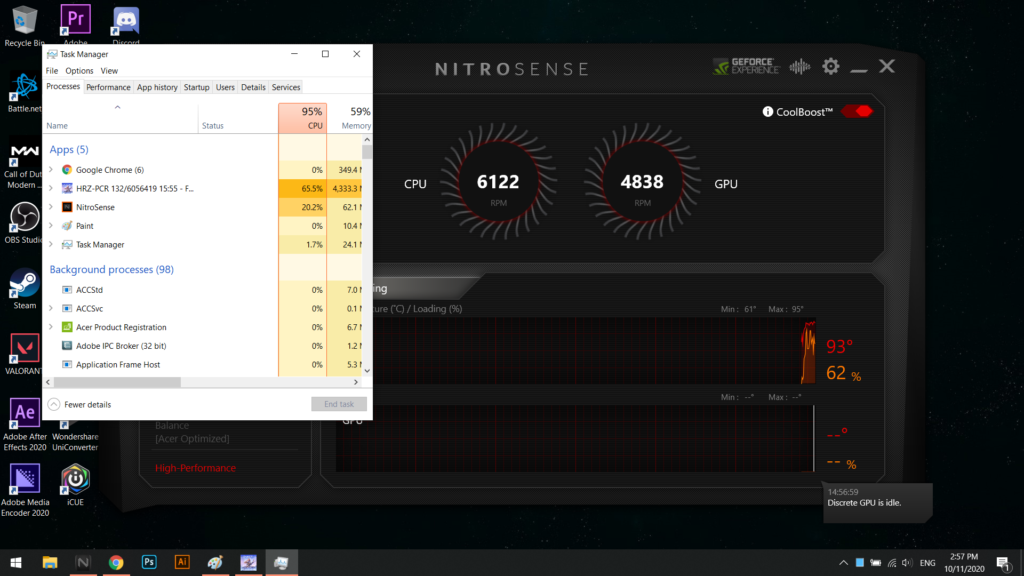
The idle state of a discrete GPU refers to periods when the GPU is not actively processing tasks or rendering graphics. During these times, the GPU operates at a lower power level and reduced clock speeds to conserve energy and minimize heat generation.
Idle state occurs when the GPU is not under load, such as when the computer is idle, running simple applications like web browsers, or displaying static images.
The GPU’s idle state is part of its power management strategy, allowing it to save energy when full processing power is not required.
Importance of Idle State for Efficiency:
Energy Efficiency:
Idle state significantly contributes to energy efficiency in computing systems, particularly in laptops and desktops. By reducing power consumption during idle periods, GPUs help extend battery life in portable devices and lower electricity costs in desktop setups.
Modern GPUs feature advanced power management technologies that dynamically adjust power usage based on workload, ensuring optimal efficiency without compromising performance when needed.
Energy efficiency is crucial not only for reducing operating costs but also for minimizing the environmental impact of computing devices.
Temperature Management:
Effective temperature management is crucial for the longevity and reliability of GPUs. During idle state, the GPU operates at lower temperatures compared to active use, reducing thermal stress on its components.
This not only improves overall system stability but also prolongs the lifespan of the GPU by minimizing wear and tear caused by heat buildup.
Efficient temperature management also helps maintain a quieter system, as cooling fans can operate at lower speeds or even remain off during idle periods.
Common Scenarios Where GPUs Are Idle:
Desktop Usage:
In everyday desktop usage scenarios, such as browsing the internet, checking emails, or working on documents, the GPU often remains in idle state. It only ramps up when performing tasks that require graphical processing power, such as photo editing or watching high-definition videos.
During idle times, the GPU conserves energy and operates quietly, contributing to a more comfortable user experience. Office environments and home users benefit significantly from this energy conservation, as it leads to lower electricity bills and a quieter working space.
Also Read: Can You Overclock A Oc Gpu – A Comprehensive Overclocking Guide!
Gaming and Multimedia:
In gaming and multimedia applications, the GPU dynamically transitions between idle and active states depending on the complexity of the graphics being rendered. During less demanding gameplay sequences, loading screens, or when viewing static content, the GPU typically enters idle mode to reduce power consumption and maintain lower temperatures.
This adaptive behavior helps balance performance and energy efficiency, ensuring smooth gameplay and multimedia experiences. Gamers often appreciate the reduced fan noise during less intensive gaming sessions, which enhances their overall experience.
Professional Workloads:
In professional environments, such as graphic design, video editing, and 3D modeling, GPUs may experience idle states during periods of low activity or when waiting for user input.
During these times, the GPU can enter an idle state to save power and reduce heat output, only ramping up when intensive tasks are performed. Professionals can benefit from lower operational costs and quieter workspaces when GPUs efficiently manage idle states.
Optimizing GPU Idle State:
Driver Settings:
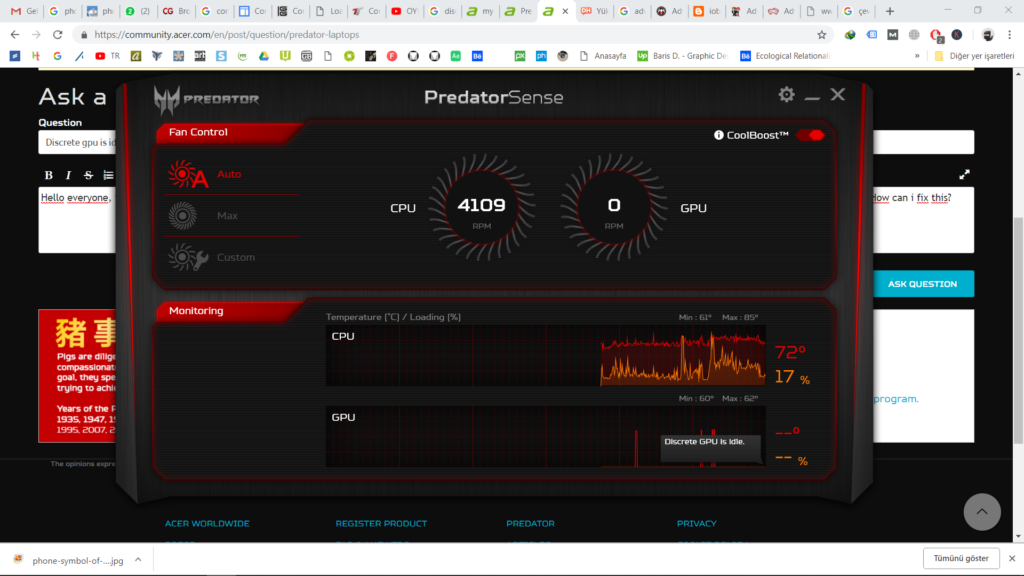
Updating GPU drivers is essential for optimizing idle states and improving overall system performance. Graphics card manufacturers frequently release driver updates that include enhancements to power management features.
These updates optimize how GPUs handle idle periods, ensuring efficient power usage without compromising responsiveness when transitioning to active use. Regularly checking for and installing driver updates can help users maintain optimal GPU performance and efficiency.
System Settings:
Users can further optimize GPU idle states by adjusting system power settings and preferences. In Windows, for example, accessing “Power Options” allows users to configure power plans that dictate how quickly the GPU enters idle mode and adjusts power consumption based on usage patterns.
Similarly, macOS offers “Energy Saver” settings that optimize energy usage during idle periods, contributing to longer battery life on compatible devices. Customizing these settings based on individual usage patterns can lead to significant improvements in energy efficiency.
Application Settings:
Certain applications, particularly those related to gaming and professional graphics work, offer settings that allow users to control how the GPU manages power and performance.
By configuring these settings, users can ensure that the GPU enters idle mode appropriately during low-demand periods, optimizing energy use and maintaining system stability. Understanding and utilizing these application-specific settings can enhance the overall efficiency of the GPU.
Advantages of Efficient GPU Idle States:
Longevity and Reliability:
Maintaining an efficient idle state enhances the longevity and reliability of the GPU. By reducing heat output and minimizing power consumption during idle periods, the GPU experiences less thermal stress and wear on its components.
This prolongs the lifespan of the graphics card and ensures consistent performance over time, benefiting both casual users and enthusiasts alike.
Efficient idle state management can lead to fewer hardware failures and reduced need for replacements, resulting in cost savings for users.
Also Read: Where To Sell Gpu – The Ultimate Guide!
Enhanced User Experience:
Efficient idle state management improves the overall user experience by ensuring quieter operation and less heat generation during non-intensive tasks. Users can enjoy a more comfortable computing environment, with reduced fan noise and cooler system temperatures, particularly in laptops and compact desktop setups.
This is especially important in environments where noise and heat can be disruptive, such as offices, classrooms, and shared living spaces.
Environmental Impact:
Optimizing GPU idle states also has positive environmental implications. By reducing energy consumption during idle periods, users contribute to lower overall electricity usage, which can help reduce the carbon footprint associated with computing.
Energy-efficient practices in GPU management align with broader sustainability goals, making it an important consideration for environmentally conscious users and organizations.
Advanced Techniques for Managing GPU Idle State:
Dynamic Frequency Scaling:
Dynamic frequency scaling, also known as dynamic voltage and frequency scaling (DVFS), is a technique used to adjust the power and performance levels of a GPU based on the current workload.
During idle periods, the GPU can lower its clock speeds and voltage to reduce power consumption and heat generation.
This technique is particularly effective in managing power use in laptops and mobile devices, where battery life is a critical concern.
Hardware Monitoring Tools:
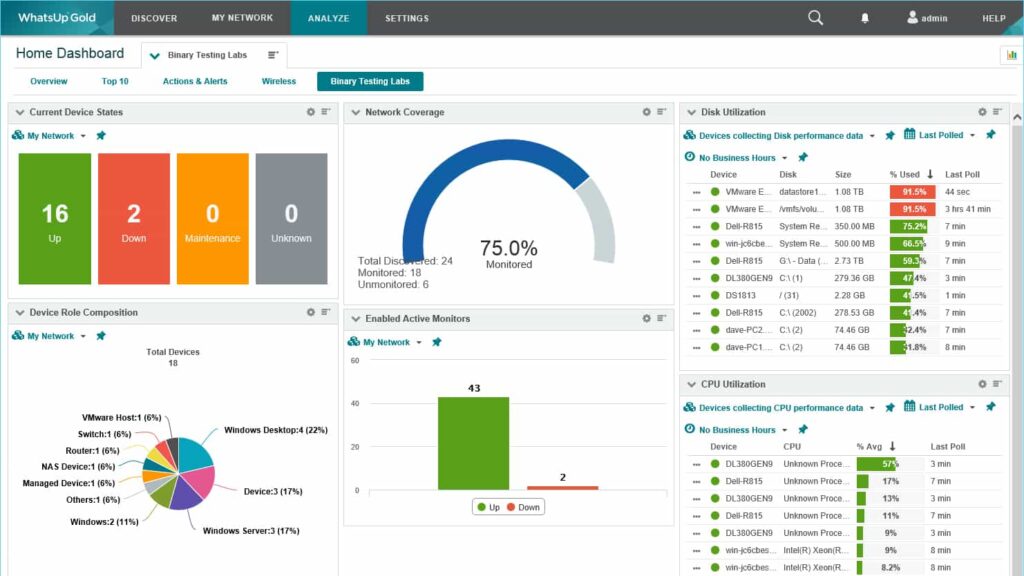
Using hardware monitoring tools, users can gain insights into the performance and power usage of their GPUs. These tools provide real-time data on GPU temperatures, clock speeds, and power consumption, allowing users to make informed decisions about optimizing idle states.
Tools like MSI Afterburner, HWMonitor, and GPU-Z are popular choices for monitoring and managing GPU performance.
Hybrid Graphics Solutions:
Some systems feature hybrid graphics solutions, combining integrated and discrete GPUs. These setups allow the system to switch between the integrated GPU for low-demand tasks and the discrete GPU for high-performance needs.
This dynamic switching helps manage power consumption more efficiently, ensuring that the discrete GPU is idle when not required, while the integrated GPU handles less demanding tasks.
FAQ’s:
1. What is a discrete GPU?
A discrete GPU is a dedicated graphics card designed for rendering visuals and handling complex graphical computations independently from the CPU.
2. What does it mean when a GPU is idle?
When a GPU is idle, it is not actively processing tasks or rendering graphics, operating at lower power levels to save energy and reduce heat.
3. Why is the idle state important for GPUs?
The idle state is important for energy efficiency, temperature management, and prolonging the lifespan of the GPU by minimizing power consumption and thermal stress during low-demand periods.
4. How can I optimize my GPU’s idle state?
You can optimize your GPU’s idle state by updating drivers, adjusting system power settings, and configuring application-specific power management options.
5. What are the benefits of efficient GPU idle states?
Efficient GPU idle states enhance energy efficiency, improve system stability, reduce heat and noise, and contribute to environmental sustainability by lowering overall electricity usage.
Conclusion:
Understanding and optimizing the idle state of discrete GPUs is crucial for energy efficiency and system performance. By effectively managing idle states, users can enjoy longer GPU lifespans, quieter operation, and reduced energy costs. Implementing strategies such as updating drivers and adjusting power settings can lead to significant benefits, making it an important aspect of GPU management for both casual and professional users.
