To ensure GPU compatibility with your motherboard, check if your motherboard has the correct PCIe slot type and version, confirm physical fit and power requirements, and update your BIOS as needed.
When upgrading or building a computer, ensuring that your GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) is compatible with your motherboard is essential for optimal performance and stability. This guide explores key factors to consider and provides detailed insights into achieving a successful GPU and motherboard pairing.
Understanding GPU and Motherboard Compatibility:

GPU and motherboard compatibility primarily hinge on the PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) slot on the motherboard. Most modern GPUs connect through a PCIe x16 slot, designed to handle high-speed data transfers crucial for gaming and professional applications.
However, older motherboards might only have PCIe x8 slots. While GPUs can function in these slots, they may not reach their full performance potential due to reduced bandwidth. It’s also important to consider the PCIe version, such as 2.0, 3.0, or 4.0.
Newer GPUs are backward compatible with older PCIe versions, but you might experience some performance limitations. Checking the specific slot type and version compatibility ensures that the GPU operates at its best with your motherboard.
Physical Space and Fit:
The physical dimensions of GPUs have evolved, with newer models often being significantly larger. Before purchasing a GPU, measure both the GPU’s dimensions and the internal space of your PC case. Many modern GPUs are quite bulky, and if your case is not spacious enough, the GPU might obstruct other components or hinder airflow.
Ensure that there is adequate clearance around the GPU for proper installation and ventilation. If space is a concern, consider opting for a GPU with a more compact design or upgrading your PC case to accommodate larger components.
Power Supply Requirements:
GPUs require substantial power to function properly. To ensure compatibility, verify the power requirements of your GPU, including the total wattage and the types of power connectors needed. Modern GPUs often require additional power through connectors such as 6-pin or 8-pin PCIe connectors.
Check that your power supply unit (PSU) can deliver the necessary wattage and has the appropriate connectors. A PSU with inadequate power output or incorrect connectors can lead to system instability or failure to power on. If your PSU is insufficient, upgrading to a higher-wattage model with the correct connectors will be necessary.
Also Read: Is BeamNG Cpu or Gpu Intensive – Ultimate Guide to BeamNG.drive Performance!
BIOS and Firmware Considerations:
Outdated BIOS or firmware can cause compatibility issues with new GPUs. Updating your motherboard’s BIOS is crucial for resolving potential problems and improving overall system stability. Manufacturers frequently release BIOS updates that include compatibility improvements and bug fixes.
Visit your motherboard manufacturer’s website to download the latest BIOS version and follow their instructions for installation. Keeping your motherboard’s firmware up-to-date is also important for ensuring full support and functionality of your GPU.
Operating System and Driver Support:
The operating system (OS) and drivers are pivotal for GPU compatibility. Ensure that you download and install the latest drivers from the GPU manufacturer’s website. Updated drivers not only enhance GPU performance but also fix bugs and support new features.
Confirm that your operating system supports the GPU and its drivers to prevent issues. For instance, some GPUs may not have drivers available for older versions of Windows or other operating systems. Keeping both the OS and drivers current will optimize GPU performance and compatibility.
Cooling Solutions and Airflow:
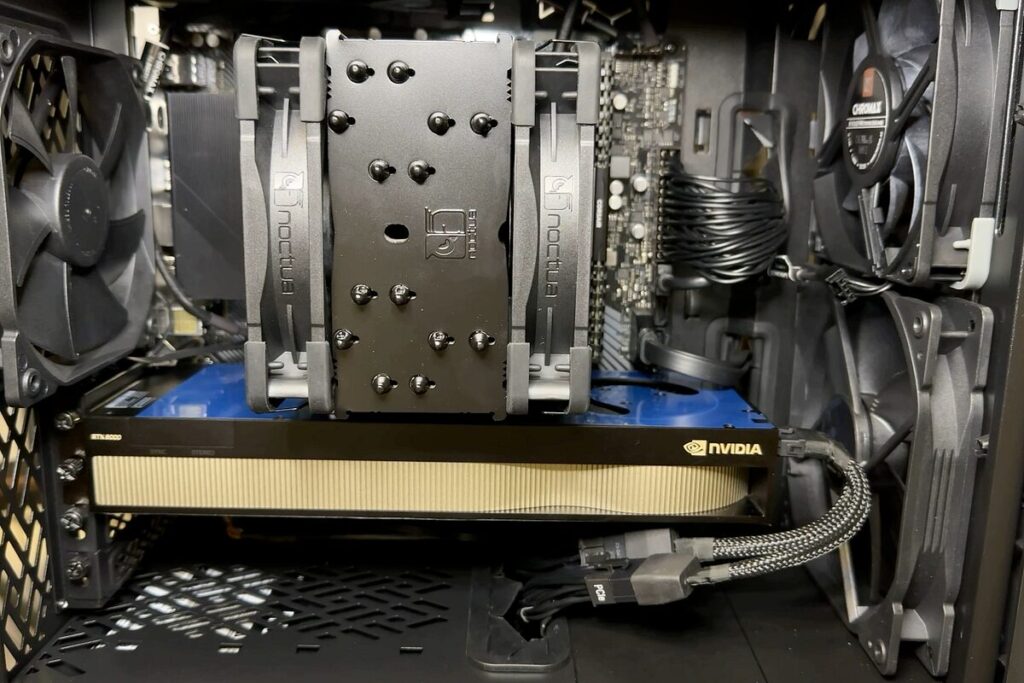
Efficient cooling is crucial when installing a new GPU, as high-performance GPUs generate significant heat. Ensure that your case has adequate airflow and that your GPU has a compatible cooling solution.
Proper ventilation helps maintain optimal temperatures and prevents overheating, which can affect performance and longevity. Consider upgrading your case fans or GPU cooling solutions if necessary to improve airflow and cooling efficiency.
Effective cooling helps ensure stable operation and extends the lifespan of your GPU and other components.
Testing Compatibility Before Purchase:
Before purchasing a GPU, it’s wise to research its compatibility with your motherboard and case. Check manufacturer specifications, user reviews, and forums where similar configurations have been tested. Compatibility lists provided by GPU and motherboard manufacturers can also be helpful.
This research helps confirm that the GPU will work seamlessly with your existing hardware and prevents potential issues after installation.
Future-Proofing Your System:
When selecting a GPU, consider future-proofing your system to accommodate upcoming technologies and upgrades. Choose a motherboard with features that support newer standards, such as additional PCIe slots and support for future memory upgrades.
Investing in a higher-quality motherboard and GPU can extend the life of your system and ensure compatibility with future hardware advancements. Future-proofing helps you maximize your investment and avoid frequent upgrades.
Also Read: How to Limit GPU Power Draw – What to Expect!
Upgrading Other Components Alongside the GPU:
Upgrading your GPU might necessitate changes to other components to ensure overall system compatibility and performance. For example, a more powerful GPU might require a higher-wattage PSU or additional cooling solutions.
Consider upgrading your CPU or RAM if you notice bottlenecks that affect performance. Coordinating upgrades across multiple components ensures a balanced and efficient system.
Monitoring and Maintenance:
Once your GPU is installed, ongoing monitoring and maintenance are essential for optimal performance. Regularly check for driver updates and system stability. Monitoring tools can help track GPU temperatures and performance metrics.
Keeping your system clean from dust and ensuring proper cooling will also contribute to long-term reliability and efficiency.
FAQ’s
1. What is the most critical factor for GPU compatibility with a motherboard?
The most critical factor is ensuring that the GPU fits into the PCIe slot on the motherboard. Check if your motherboard has a PCIe x16 slot and verify its version compatibility.
2. Can a GPU with PCIe 3.0 work in a PCIe 2.0 slot?
Indeed, PCIe 3.0 GPUs can be used with PCIe 2.0 slots; however, because of the lower bandwidth, their performance might not be as good as it could be.
3. How can I check if my power supply is adequate for a new GPU?
Verify the GPU’s power requirements and ensure your PSU provides enough wattage and has the necessary power connectors, such as 6-pin or 8-pin PCIe connectors.
4. Why is updating the motherboard BIOS important for GPU compatibility?
Updating the BIOS can resolve compatibility issues, improve system stability, and ensure that the motherboard fully supports the GPU’s features.
5. How can I determine if my GPU will physically fit in my case?
Measure the dimensions of the GPU and compare them to the available space in your PC case. Ensure there is enough clearance for the GPU and proper airflow.
Conclusion
Ensuring compatibility between your GPU and motherboard involves multiple factors, including PCIe slot type, physical dimensions, power requirements, and BIOS updates. By carefully checking these elements, you can achieve optimal performance and stability. Proper research and preparation will help you integrate a new GPU seamlessly into your system and avoid potential issues, ensuring a smooth computing experience.