GPU sagging can potentially cause physical damage to your GPU and motherboard if not addressed. Using support brackets or reinforced PCIe slots can prevent this issue effectively.
Graphics card sag, often referred to as GPU sag, is a common issue in many desktop computers. It occurs when the graphics card, due to its weight, bends downward, creating a sagging effect. But is GPU sagging bad? Let’s explore this topic in detail, covering the causes, risks, prevention methods, and solutions.
What Causes GPU Sagging?
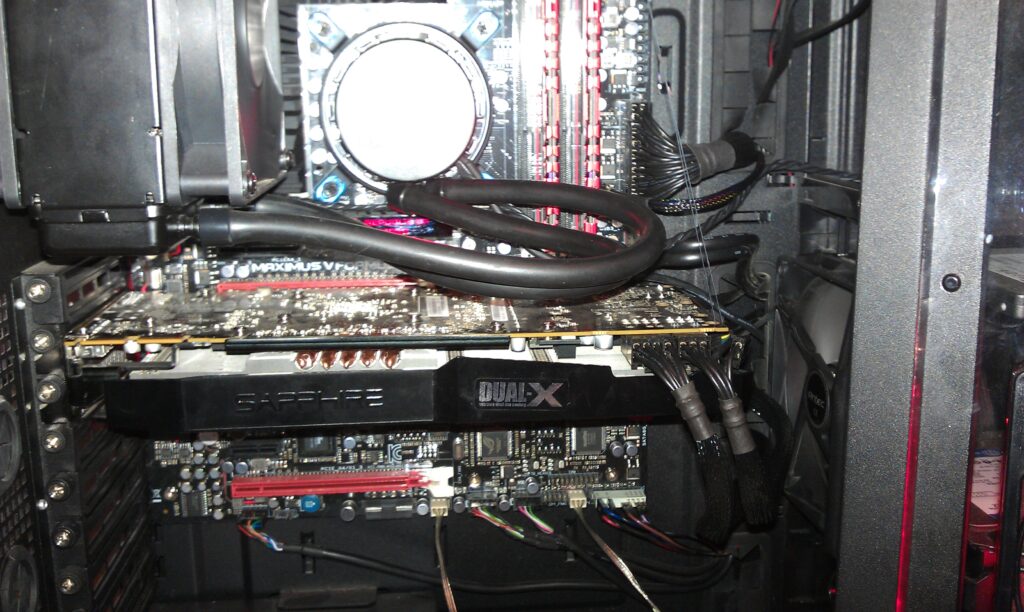

GPU sagging is primarily caused by the weight of the graphics card itself. High-end GPUs are often large and heavy, and when mounted horizontally, the unsupported end tends to droop. This sagging effect is exacerbated by several factors.
Weak PCIe slots can contribute significantly to GPU sagging. Older or lower-quality motherboards may have PCIe slots that are less supportive, unable to handle the weight of modern, high-performance GPUs. Inadequate case support is another common issue.
Some computer cases do not provide sufficient structural support for heavy GPUs, leading to sagging over time. Additionally, poor mounting techniques during installation can also contribute to GPU sagging. Incorrectly installed GPUs may not be adequately secured, increasing the likelihood of sagging.
Potential Risks of GPU Sagging:
The most immediate concern with GPU sagging is the potential for physical damage. Over time, the weight of the GPU can strain the PCIe slot, leading to possible motherboard damage or failure. The GPU itself might also suffer from stress fractures or connector damage. The connectors and solder points on the GPU can experience undue stress, potentially leading to long-term damage or failure.
While less common, severe GPU sagging can lead to connectivity issues. A misaligned GPU may not make proper contact with the PCIe slot, causing intermittent performance problems or crashes. This can manifest as random system crashes, graphical glitches, or other performance issues that can be difficult to diagnose.
Additionally, for many PC enthusiasts, a sagging GPU is simply an eyesore. It disrupts the clean, organized look of a well-built system, which can be particularly bothersome in systems with side panel windows or RGB lighting. Aesthetics play a significant role in modern PC builds, and a sagging GPU can detract from the overall appearance of the system.
How to Prevent GPU Sagging:
One of the most effective ways to prevent GPU sagging is by using a support bracket. These brackets are designed to hold up the end of the GPU, distributing its weight more evenly and reducing strain on the PCIe slot. Support brackets are available in various designs and can be easily installed to provide immediate support to a sagging GPU.
If your case supports it, installing the GPU vertically can eliminate sagging. This orientation naturally supports the weight of the GPU, preventing it from drooping. Vertical GPU mounts are becoming more common in modern cases and can be a stylish and effective solution to GPU sagging.
Some motherboards come with reinforced PCIe slots designed to handle heavy GPUs better. If you’re planning a new build, consider a motherboard with this feature. Reinforced PCIe slots provide additional support and stability for heavy GPUs, reducing the risk of sagging.
For those who prefer DIY solutions, there are various creative fixes. Some builders use zip ties, custom-made brackets, or even Lego pieces to prop up their GPUs.
While not always elegant, these solutions can be effective. DIY fixes can be a cost-effective way to address GPU sagging, but they may not always provide the best long-term solution.
Also Read: How To Know If GPU Will Fit In Case – A Comprehensive Guide!
Addressing Existing GPU Sagging:
If you’re already experiencing GPU sagging, there are steps you can take to address it. First, ensure that the GPU is properly seated in the PCIe slot and that all screws are tight. Sometimes, simply re-seating the GPU and tightening the screws can alleviate minor sagging issues.
Installing a support bracket can help mitigate sagging in an existing setup. Many support brackets are adjustable and can be easily added to a system without requiring significant modifications. This can provide immediate relief to a sagging GPU and prevent further damage.
Sometimes, adjusting the placement of power cables can help support the GPU. Proper cable management can reduce the downward pull on the GPU, helping to alleviate sagging. Ensuring that power cables are routed in a way that minimizes their impact on the GPU can be a simple yet effective solution.
Regularly check for any signs of damage to the GPU or motherboard. Taking these steps can help maintain the stability and performance of your system. Monitoring the condition of your components can help you identify and address issues before they become serious problems.
Why GPU Sagging Happens More in Modern Builds?
Modern GPUs are becoming increasingly powerful, which often means they are larger and heavier. This added weight contributes to the sagging issue. Additionally, aesthetic trends such as tempered glass cases and RGB lighting encourage builders to display their components, making sagging more noticeable.
As GPUs continue to evolve, the challenge of managing their weight becomes more significant. Larger cooling solutions and additional features, such as backplates and RGB lighting, add to the overall weight of the GPU, exacerbating sagging issues.
Impact on System Cooling:
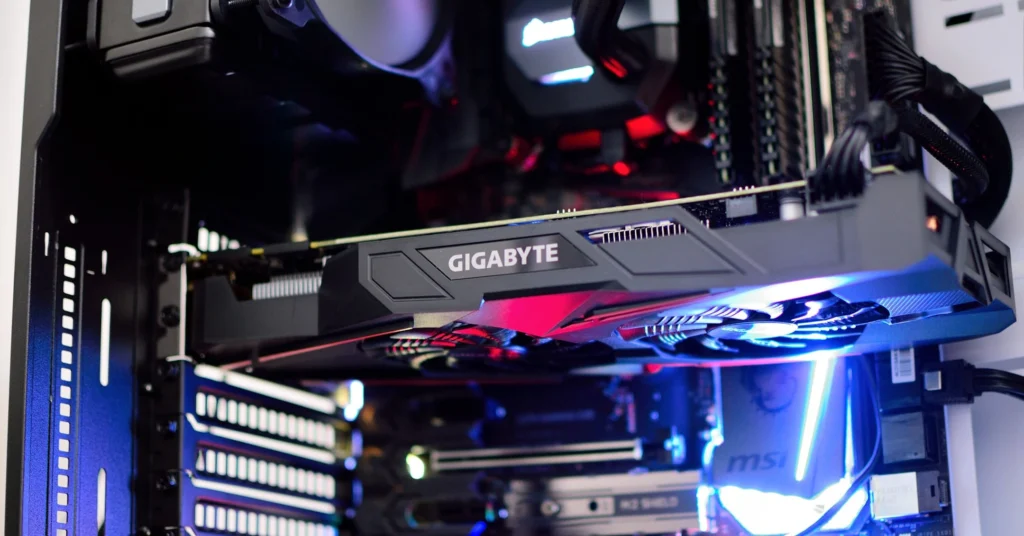

GPU sagging can also affect your system’s cooling efficiency. A sagging GPU might obstruct airflow within the case, leading to higher temperatures and reduced cooling performance. Ensuring that the GPU remains level can help maintain optimal airflow and cooling efficiency.
Proper cooling is essential for maintaining the performance and longevity of your components. A sagging GPU that disrupts airflow can cause other components, such as the CPU and motherboard, to run hotter, potentially reducing their lifespan.
Long-Term Effects of Ignoring GPU Sagging:
Ignoring GPU sagging can lead to long-term damage to your computer. The constant strain on the PCIe slot can cause it to wear out prematurely, leading to potential failures. Additionally, the GPU itself may develop stress fractures or other forms of damage over time.
Addressing GPU sagging promptly can help avoid these long-term issues. Regular maintenance and monitoring can help you catch and address GPU sagging before it causes significant damage.
FAQ’s
1. What is GPU sagging?
GPU sagging occurs when the weight of a graphics card causes it to bend downward, creating a sagging effect in a computer case.
2. What causes GPU sagging?
GPU sagging is primarily caused by the weight of the GPU itself, especially high-end models, and inadequate support from the PCIe slot or case.
3. Can GPU sagging damage my computer?
Yes, over time, GPU sagging can strain the PCIe slot, leading to potential motherboard damage or GPU connector damage.
4. How can I prevent GPU sagging?
You can prevent GPU sagging by using support brackets, installing the GPU vertically, using a motherboard with reinforced PCIe slots, or employing creative DIY solutions.
5. Does GPU sagging affect system cooling?
Yes, GPU sagging can obstruct airflow within the case, leading to higher temperatures and reduced cooling efficiency for your system.
Conclusion:
While GPU sagging is a common issue, it can lead to serious problems if ignored. By using support brackets, ensuring proper installation, and regularly checking for signs of damage, you can prevent or address GPU sagging effectively. Taking these steps will help maintain the stability and performance of your system, ensuring its longevity.