Your GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) is a vital component of your computer, responsible for rendering images, video, and animations. However, if you notice unusually high temperatures, it could signal potential issues that need immediate attention.
High GPU temperatures can indicate underlying issues that need immediate attention. Common causes include poor ventilation, overclocking, high ambient temperatures, faulty cooling, high workloads, thermal paste degradation, and poor case design.
This comprehensive guide explores the common causes of high GPU temperatures and offers detailed solutions to keep your system running smoothly.
Poor Ventilation and Airflow:

Cause: Limited airflow in your PC case can lead to heat buildup, causing your GPU to overheat.
Solution:
- Clean Your Case: Dust and debris can block airflow and hinder the cooling process. Regularly clean the inside of your PC case and ensure fans are dust-free. Use compressed air to remove dust from hard-to-reach areas.
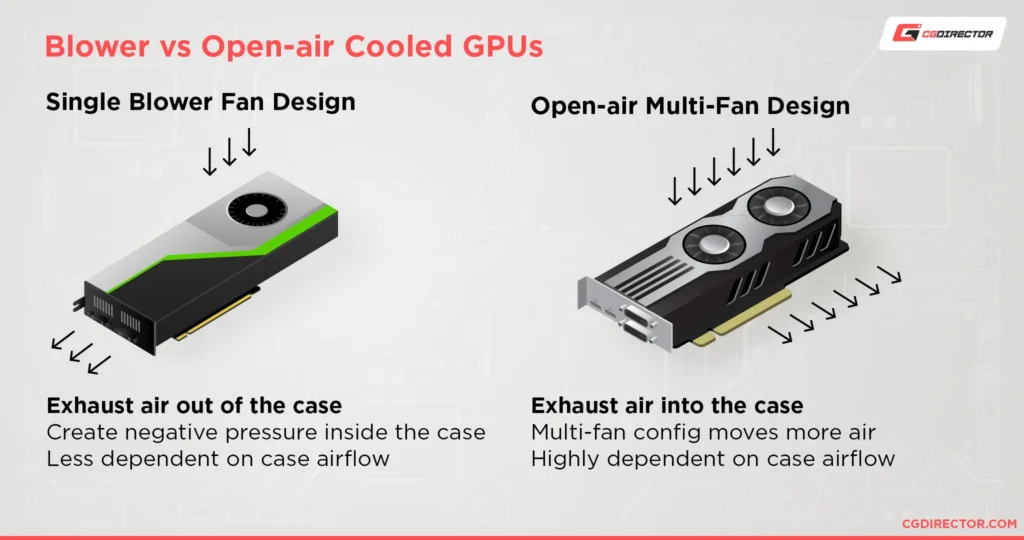
- Optimize Fan Placement: Ensure your fans are correctly positioned to create an effective airflow path. Intake fans should bring cool air in, and exhaust fans should push hot air out. Adding more fans or upgrading to higher-quality fans can also improve airflow.
- Cable Management: Properly organize and tie down cables to minimize obstruction to airflow. This can enhance cooling efficiency and reduce heat buildup.
Overclocking:
Cause: Overclocking your GPU can significantly increase performance but also generates more heat.
Solution:
- Revert Overclocking: If your GPU is running too hot, consider returning to its default settings. Use software like MSI Afterburner or EVGA Precision X1 to adjust settings.
- Efficient Cooling: If you must overclock, invest in superior cooling solutions, such as high-performance aftermarket GPU coolers. Water cooling systems can provide better temperature control compared to air coolers.
- Incremental Overclocking: Gradually increase your GPU’s clock speed and monitor temperatures to ensure stability and safe operating temperatures.
High Ambient Temperature:
Cause: The temperature of your environment affects your GPU temperature. Hotter room temperatures can lead to higher GPU temperatures.
Solution:
- Cool Your Room: Use air conditioning or fans to lower the room temperature. Keeping your workspace cool can help maintain optimal GPU temperatures.
- Relocate Your PC: Place your PC in a cooler, well-ventilated area. Avoid placing it near heat sources or in direct sunlight.
- Open Windows: If the external temperature is lower than the internal room temperature, opening windows can help improve airflow and reduce overall room temperature.
Faulty or Insufficient Cooling:
Cause: A malfunctioning GPU fan or insufficient cooling system can cause your GPU to overheat.
Solution:
- Check GPU Fans: Ensure the GPU fans are working correctly. Listen for unusual noises that might indicate a malfunction. Replace them if they are faulty.
- Upgrade Cooling Systems: Consider upgrading to a more efficient cooling system, such as liquid cooling or better-quality air coolers. Hybrid cooling solutions that combine air and liquid cooling can also be effective.
- Thermal Pads: Check the thermal pads on the VRMs and memory chips of your GPU. Replacing worn-out thermal pads can improve heat dissipation.
Also Read: Is Cod CPU Or GPU Intensive – Which Matters More!
High Workload:
Cause: Intensive tasks like gaming, video editing, or mining can push your GPU to its limits, generating more heat.
Solution:
- Monitor Workload: Use software to monitor your GPU’s workload and temperature. Programs like HWMonitor, GPU-Z, and MSI Afterburner can provide real-time data.
- Adjust Settings: Lowering the graphics settings in games or software can reduce the GPU load and heat generation. Enable features like V-Sync to cap the frame rate and reduce workload.
- Workload Distribution: Distribute intensive tasks over time to prevent prolonged periods of high GPU usage. This can help manage heat buildup.
Thermal Paste Degradation:
Cause: Over time, the thermal paste between your GPU and its heatsink can degrade, reducing its ability to transfer heat effectively.
Solution:
- Replace Thermal Paste: Apply new thermal paste to ensure effective heat transfer. This can significantly lower your GPU temperatures. Use high-quality thermal paste, such as Arctic Silver 5 or Noctua NT-H1, for optimal results.
- Application Method: Apply a pea-sized amount of thermal paste to the GPU die and spread it evenly. Avoid using too much paste, as it can reduce efficiency.
Case Design:
Cause: Some PC cases have poor designs that restrict airflow and trap heat.
Solution:
- Choose a Better Case: Invest in a PC case designed for optimal airflow with ample ventilation and multiple fan mounts. Look for cases with mesh panels or dedicated airflow channels.
- Modify Existing Case: If buying a new case isn’t an option, consider modifying your current one by adding more fans or cutting vents for better airflow. Side panel fans and top-mounted exhaust fans can improve ventilation.
- Positive Pressure: Aim for positive pressure inside the case by having more intake fans than exhaust fans. This helps keep dust out and ensures cooler air flows through the components.
Additional Tips for Managing GPU Temperatures:
- Regular Monitoring: Keep an eye on your GPU temperatures using monitoring software. Set up alerts for when temperatures exceed safe thresholds.
- Fan Curves: Customize fan curves in your GPU management software to increase fan speed at lower temperatures. This can help preemptively cool the GPU before it gets too hot.
- BIOS Update: Ensure your GPU BIOS is up-to-date. Manufacturers often release updates that improve fan control and thermal management.
- Undervolting: Undervolting your GPU can reduce power consumption and heat generation without significantly affecting performance. Tools like MSI Afterburner can help with this process.
- Power Supply: Ensure your power supply unit (PSU) is adequate for your system’s power needs. An underpowered PSU can cause instability and increased heat output.
FAQ’s
1. What can cause my GPU temperature to be high?
High GPU temperatures can be caused by poor ventilation, overclocking, high ambient temperatures, faulty or insufficient cooling, high workloads, thermal paste degradation, and poor case design.
2. How can I improve ventilation and airflow in my PC case?
Regularly clean the inside of your PC case, ensure fans are dust-free, optimize fan placement, and properly manage cables to enhance airflow and reduce heat buildup.
3. What should I do if overclocking is causing my GPU to overheat?
Consider reverting to default settings, investing in superior cooling solutions, or incrementally increasing your GPU’s clock speed while monitoring temperatures to ensure stability and safe operating temperatures.
4. How does high ambient temperature affect my GPU?
High ambient temperatures can lead to higher GPU temperatures. To mitigate this, cool your room with air conditioning or fans, relocate your PC to a cooler area, or open windows to improve airflow.
5. When should I replace the thermal paste on my GPU?
Replace the thermal paste if your GPU is overheating and it has been a long time since it was last replaced. High-quality thermal paste can improve heat transfer and significantly lower GPU temperatures.
Conclusion
High GPU temperatures can impact your system’s performance and longevity. By understanding the causes and implementing these solutions, you can keep your GPU running at optimal temperatures, ensuring a smooth and efficient computing experience. Regular maintenance and monitoring are key to preventing overheating issues and preserving your hardware’s health.