Both the CPU and GPU play crucial roles in VR: the CPU manages system operations and game logic, while the GPU handles rendering and visual quality.
Virtual Reality (VR) technology has transformed digital experiences, immersing users in simulated environments that feel remarkably real. Whether exploring virtual worlds, participating in training simulations, or enjoying interactive entertainment, VR relies heavily on the hardware that powers it to deliver seamless and immersive experiences.
Understanding VR Components
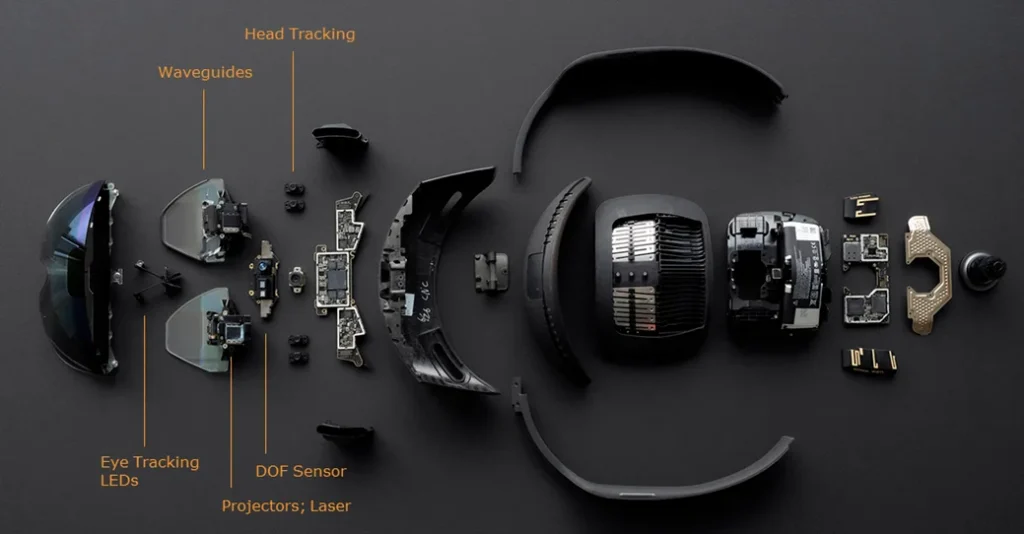

A VR system consists of several essential components working together seamlessly to create immersive experiences. At its core is the VR headset, which serves as the user’s window into the virtual world. Equipped with high-resolution displays and motion-tracking sensors, the headset enables users to view and interact with the virtual environment in a way that simulates real-life experiences.
Complementing the headset are controllers that allow users to manipulate objects and navigate within the virtual space, providing tactile feedback and enhancing immersion. The entire VR experience is driven by a powerful PC or console, responsible for rendering graphics, processing inputs, and maintaining overall system performance throughout the VR session.
CPU vs. GPU: Their Roles in VR
In the realm of VR, both the CPU (Central Processing Unit) and GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) play crucial roles, albeit in different capacities.
CPU (Central Processing Unit)
The CPU acts as the brain of the system, handling tasks such as game logic, physics calculations, and system management. It ensures smooth operation by processing inputs from controllers, managing memory, and coordinating various components of the VR setup.
While the CPU’s role is indispensable in maintaining system stability and managing non-graphics-related tasks, its impact on graphical performance is less pronounced compared to the GPU.
GPU (Graphics Processing Unit)
Conversely, the GPU is dedicated to rendering graphics and visual effects in real-time, making it essential for delivering high-quality visuals and maintaining smooth frame rates in VR.
Tasks such as rendering complex 3D environments, applying textures, and processing shaders fall within the domain of the GPU. Its ability to handle these intensive graphical computations directly influences the visual fidelity and immersion levels experienced by users in VR applications.
Importance of CPU and GPU in VR

Both the CPU and GPU contribute uniquely to the overall VR experience, with each playing a critical role depending on the nature of the task at hand. The CPU’s importance lies in its ability to manage game logic, handle system-level tasks, and process inputs from various peripherals. It ensures that interactions within the virtual environment are responsive and seamless, contributing to overall user comfort and immersion.
On the other hand, the GPU’s primary importance stems from its role in rendering detailed visuals, maintaining high frame rates, and enhancing the overall visual quality of VR applications. A powerful GPU is crucial for delivering immersive experiences by ensuring that virtual environments appear lifelike and respond fluidly to user interactions.
System Requirements for VR
Optimizing the VR experience requires hardware that meets or exceeds recommended specifications, tailored to the complexity and demands of VR applications. Minimum requirements typically include a capable CPU and GPU combination that can handle basic VR tasks, such as 360-degree videos or simple simulations.
For more demanding VR experiences, such as high-end gaming or professional simulations, a robust setup featuring a high-performance CPU, powerful GPU, ample RAM, and fast storage is recommended. This ensures that users can enjoy smooth performance, high visual fidelity, and minimal latency during their VR sessions.
Balancing CPU and GPU for Optimal VR Performance
Achieving optimal performance in VR involves striking a balance between CPU and GPU capabilities, ensuring that both components work synergistically to deliver a seamless and immersive experience. Compatibility between CPU, GPU, and VR headset specifications is essential to avoid performance bottlenecks and maximize the potential of each component.
Additionally, investing in adequate cooling solutions and a reliable power supply unit (PSU) helps maintain system stability and performance under heavy VR loads. Upgrading hardware components periodically allows users to leverage advancements in CPU and GPU technology, ensuring that their VR setup remains capable of handling future VR applications and experiences.
Advanced Considerations for VR Performance

To further enhance the VR experience, users can explore advanced optimization techniques and best practices. This includes carefully overclocking CPU and GPU components to boost performance, while ensuring adequate cooling to prevent overheating.
Regular updates to graphics drivers and VR software are recommended to benefit from performance optimizations, bug fixes, and new features that enhance compatibility and stability. Creating a dedicated play area with sufficient space and minimal obstructions enhances safety and usability during VR sessions, allowing users to fully immerse themselves in the virtual environment without interruptions.
FAQs:
1. What is the role of the CPU in VR?
The CPU handles game logic, physics calculations, and system management in VR, ensuring smooth operation and responsiveness.
2. Why is the GPU important in VR?
The GPU is essential for rendering detailed graphics, maintaining high frame rates, and enhancing visual quality in VR applications.
3. What are the minimum hardware requirements for VR?
Minimum requirements include a capable CPU and GPU, sufficient RAM, and fast storage to handle basic VR tasks effectively.
4. How can I optimize CPU and GPU performance for VR?
Optimizing involves balancing hardware capabilities, ensuring compatibility with VR headset specifications, and investing in adequate cooling and power solutions.
5. Why is system stability important in VR setups?
Stable performance prevents interruptions and enhances immersion in VR by ensuring consistent frame rates and responsive interactions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the collaboration between the CPU and GPU is crucial for creating immersive VR environments. While the CPU oversees fundamental operations and logic within the system, the GPU excels in rendering intricate visuals and sustaining fluid performance. By optimizing these components and adhering to recommended specifications, users can experience seamless interactions and exceptional visual fidelity in VR applications. Investing in a well-balanced and robust system ensures that VR experiences are not only responsive but also captivating, enhancing overall user enjoyment and satisfaction.