GPU fans can either push air onto the heatsinks or pull air away, depending on the cooler’s design, to optimize cooling efficiency.
Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) are essential components in modern computers, particularly for gaming, video editing, and other graphic-intensive tasks. A crucial aspect of maintaining optimal GPU performance is understanding the cooling system, especially the role of GPU fans.
One common question is whether GPU fans push or pull air. This article will delve into the mechanics of GPU fans and how they contribute to cooling your GPU.
Understanding GPU Cooling Systems
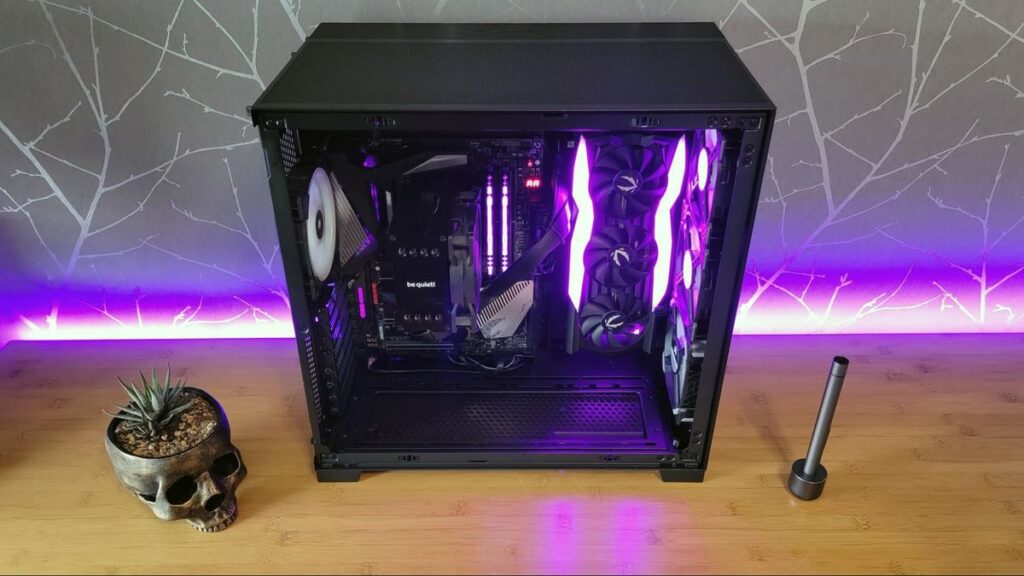

GPUs generate a significant amount of heat during operation, which can impact performance and longevity if not properly managed. The cooling system of a GPU typically consists of heatsinks and fans.
The heatsinks absorb heat from the GPU, and the fans help dissipate this heat by moving air across the heatsinks.
The Role of GPU Fans
GPU fans are designed to manage airflow in a specific manner to ensure efficient cooling. The direction in which the fans move air—whether they push air onto the heatsink or pull air away from it—can vary depending on the design of the GPU cooler.
Push Configuration
In a push configuration, the fans are positioned to blow air directly onto the heatsinks. This approach forces cool air over the heatsinks, effectively absorbing heat from the GPU. The heated air is then expelled from the GPU and typically vented out of the computer case.
This configuration is commonly seen in blower-style coolers, where the fan pushes air through the heatsink and exhausts it out of the back of the card. This setup is advantageous in small or poorly ventilated cases, as it prevents hot air from recirculating inside the case.
Pull Configuration
In a pull configuration, the fans are set up to draw hot air away from the heatsinks. This method pulls the heated air through the heatsinks and away from the GPU, allowing cooler air to take its place. The warm air is then expelled from the pc case.
Pull configurations are often used in open-air coolers, where multiple fans work together to pull hot air away from the heatsinks and exhaust it out of the case. This setup is more efficient in cases with good airflow, as it relies on the case fans to remove the hot air.
Also Read: Do GPU Brands Matter – Unveiling the Truth!
Common GPU Fan Configurations
Most modern GPUs use a combination of both push and pull configurations to optimize cooling. Here are a few common setups:
- Blower-Style Coolers: These GPUs feature a single fan that pushes air through the heatsink and out the back of the card, expelling hot air directly out of the computer case. This configuration is efficient for systems with limited airflow.
- Open-Air Coolers: These GPUs have multiple fans that push air directly onto the heatsink. The hot air is then dissipated into the case and removed by the case fans. This configuration is ideal for cases with good airflow.
- Hybrid Coolers: Some high-end GPUs combine liquid cooling with air cooling. The liquid cooler handles most of the heat, while the fans push and pull air to manage any residual heat.
Factors Influencing GPU Fan Performance
Several factors can influence the performance of GPU fans, including:
- Fan Size and Speed: Larger fans can move more air at lower speeds, reducing noise levels while maintaining cooling efficiency. Smaller fans need to spin faster to move the same amount of air, which can increase noise.
- Heatsink Design: The design and material of the heatsink can impact how effectively it dissipates heat. Copper heatsinks, for example, are more efficient at heat transfer than aluminum ones. The fin density and surface area also play a crucial role in heat dissipation.
- Case Airflow: Proper case ventilation is crucial. Good airflow ensures that hot air is efficiently expelled from the case, preventing it from being recirculated. This involves strategically placing
intake and exhaust fans to create a balanced airflow pattern.
- Thermal Paste Quality: The thermal paste between the GPU and the heatsink affects heat transfer. High-quality thermal paste can improve cooling performance by ensuring efficient heat transfer.
Improving GPU Cooling Efficiency
To optimize your GPU cooling, consider the following tips:
- Maintain Cleanliness: Dust buildup can impede airflow and reduce cooling efficiency. Regularly clean your GPU and case fans to ensure optimal performance. Dust filters on intake fans can also help keep the inside of your case clean.
- Improve Case Airflow: Ensure your computer case has adequate airflow by using multiple intake and exhaust fans. This helps maintain a consistent flow of cool air and efficient expulsion of hot air. Avoid obstructing airflow with cables or other components.
- Monitor Temperatures: Use software tools to monitor your GPU temperatures. If temperatures are consistently high, consider adjusting fan speeds or adding additional cooling solutions. Many GPUs come with software that allows you to customize fan curves for better cooling performance.
- Upgrade Cooling Solutions: If your GPU is still running hot despite optimizing airflow, consider upgrading your cooling solution. Aftermarket GPU coolers, additional case fans, or even liquid cooling can significantly improve temperatures.
Benefits of Optimal GPU Cooling
Ensuring your GPU is adequately cooled has several benefits:
- Enhanced Performance: Lower temperatures allow the GPU to maintain higher clock speeds without throttling, resulting in better performance in games and applications.
- Longevity: Proper cooling reduces thermal stress on the GPU components, potentially extending the lifespan of your graphics card.
- Stability: Cooler GPUs are less likely to experience crashes or instability during intense workloads.
FAQs:
1. Do GPU fans push or pull air?
GPU fans can either push air onto the heatsinks or pull air away from them, depending on the cooler’s design.
2. What is a push configuration for GPU fans?
In a push configuration, fans blow air directly onto the heatsinks, forcing cool air over them and expelling heated air out of the case.
3. What is a pull configuration for GPU fans?
In a pull configuration, fans draw hot air away from the heatsinks, pulling the heated air through and expelling it from the case.
4. Which GPU cooler type uses a push configuration?
Blower-style coolers typically use a push configuration, where a single fan pushes air through the heatsink and out the back of the card.
5. How can I optimize my GPU cooling?
Maintain cleanliness, improve case airflow, monitor temperatures, and consider upgrading cooling solutions if necessary.
Conclusion:
Understanding whether GPU fans push or pull air is crucial for optimizing cooling and maintaining GPU performance. Most GPUs use a combination of both configurations based on their design. Keeping your system clean, ensuring good case airflow, and monitoring temperatures will help keep your GPU cool and extend its lifespan. Proper GPU cooling is essential for achieving the best performance and longevity.
